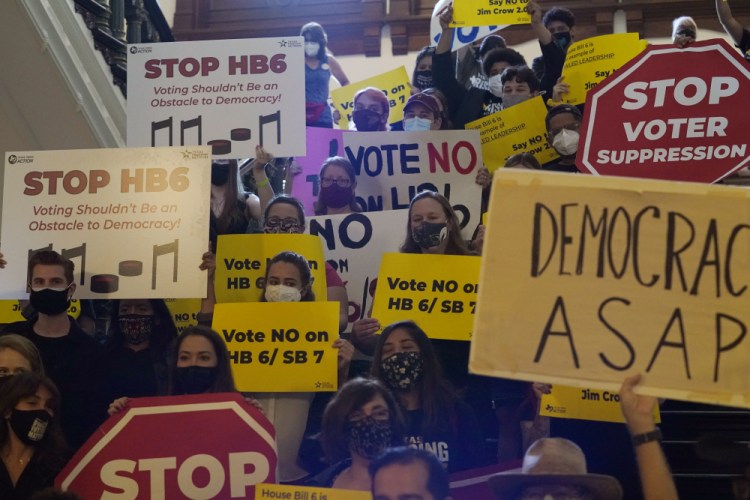
AUSTIN, Texas — Texas Republicans dug in Saturday for a final weekend vote on some of the most restrictive new voting laws in the U.S., putting the last touches on a sweeping bill that would eliminate drive-thru voting, empower partisan poll watchers and limit voting on Sundays, when many Black churchgoers head to the polls.
The changes would need to be approved before midnight on Sunday, when the GOP-controlled Legislature wraps up a session dominated by Republicans muscling through staunchly conservative measures pertaining to guns, abortion and how race can be taught in public schools.
But none has drawn backlash like Senate Bill 7, which Republicans packed with a raft of new voting restrictions that would alter how the country’s biggest red state conducts elections. Democrats have virtually no path to stop it from passing, thereby putting Republicans on the brink of a major victory in their nationwide campaign to impose new voting restrictions driven by former President Donald Trump’s false claims that the 2020 election was stolen from him.
Republican Gov. Greg Abbott has said he will sign the measure, which Democrats have said they would challenge in court.
President Biden released a statement calling the Texas bill’s final form “wrong and un-American.”
“Today, Texas legislators put forth a bill that joins Georgia and Florida in advancing a state law that attacks the sacred right to vote. It’s part of an assault on democracy that we’ve seen far too often this year – and often disproportionately targeting Black and Brown Americans,” Biden said.
The final version of the bill was hashed out behind closed doors by negotiators from the state House and Senate, nearly all of whom were Republicans. They preserved the elimination of 24-hour polling stations and drive-thru voting centers, both of which Harris County, the state’s largest Democratic stronghold, introduced last year in an election that saw record turnout.
GOP legislators are also moving to prohibit Sunday voting before 1 p.m., which critics called an attack on what is commonly known as “souls to the polls” – a get-out-the vote campaign used by Black church congregations nationwide. The idea traces back to the civil rights movement. Gary Bledsoe, president of the NAACP of Texas, said the provision is “clearly intended to limit the Sunday vote” and would result in longer afternoon lines at polling places.
Texas is also set to newly empower partisan poll watchers, allowing them more access inside polling places and threatening criminal penalties against elections officials who restrict their movement. Republicans originally proposed giving poll watchers the right to take photos, but that language was removed from the final bill that lawmakers were set to vote on this weekend.
Major corporations, including Texas-based American Airlines and Dell, have warned that the measures could harm democracy and the economic climate. But Republicans shrugged off their objections, and some cases, ripped business leaders for speaking out.
The top Republican negotiators, state Sen. Bryan Hughes and state Rep. Briscoe Cain, called the bill “one of the most comprehensive and sensible election reform bills” in Texas’ history.
“Even as the national media minimizes the importance of election integrity, the Texas Legislature has not bent to headlines or corporate virtue signaling,” they said in a joint statement.
Texas already has some of the country’s tightest voting restrictions and is regularly cited by nonpartisan groups as a state where it is especially hard to vote. It was one of the few states that did not make it easier to vote by mail during the pandemic.
It is also the last big battleground in Republicans’ efforts to tighten voting laws around the country. Florida, Georgia, and Arizona have also approved new voting restrictions in recent months.
Since Trump’s defeat, at least 14 states have enacted more restrictive voting laws, according to the New York-based Brennan Center for Justice. It has also counted nearly 400 bills filed this year nationwide that would restrict voting.
Republican lawmakers in Texas have insisted that the changes are not a response to Trump’s false claims of widespread fraud but are needed to restore confidence in the voting process. But doubts about the election’s outcome have been fanned by some of the state’s top GOP leaders, including Attorney General Ken Paxton, who led a failed lawsuit at the U.S. Supreme Court to try to overturn the election.
Lt. Gov. Dan Patrick, who chaired Trump’s presidential campaign in Texas, offered a $1 million reward to anyone who could produce evidence of voter fraud. Nonpartisan investigations of previous elections have found that voter fraud is exceedingly rare. State officials from both parties, including in Texas, as well as international observers have also said the 2020 election went well.
Send questions/comments to the editors.